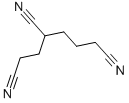
1,3,6-HEXANETRICARBONITRILE CAS#: 1772-25-4; ChemWhat Code: 112490
Identification
| Patent Information | ||
| Patent ID | Title | Publication Date |
| CN115784927 | Preparation method of alkane trinitrile | 2023 |
| US2021/408602 | ELECTROLYTE AND ELECTROCHEMICAL DEVICE | 2021 |
| US4128571 | Thermal conversion of 4-cyano-suberonitrile to acrylonitrile | 1978 |
| US5132427 | Process for the preparation of amines | 1992 |
Physical Data
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow oily liquid |
| Boiling Point, °C | Pressure (Boiling Point), Torr |
| 186 – 200 | 0.2 |
Spectra
| Description (NMR Spectroscopy) | Nucleus (NMR Spectroscopy) | Solvents (NMR Spectroscopy) | Frequency (NMR Spectroscopy), MHz |
| Chemical shifts | 1H | chloroform-d1 | |
| Chemical shifts | 13C | chloroform-d1 | |
| Chemical shifts | 1H | chloroform-d1 | 400 |
Route of Synthesis (ROS)
| Conditions | Yield |
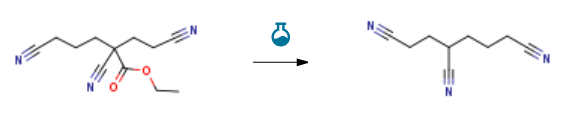
| With water; sodium chloride In dimethyl sulfoxide at 160℃; Reagent/catalyst; Temperature; Solvent; Experimental Procedure 4-8 Preparation of 1,3,6-hexane trinitrile Take 50 grams of 2,5-dicyano-2-cyanoethyl-pentanoic acid ethyl ester prepared in Example 1, add 100 grams of DMSO, add 8 grams of water, 2.5 grams of NaCl, and raise the temperature to 160°C.After the gas no longer overflowed, the DMSO and water were removed by concentration under reduced pressure, and then the distillation was continued to obtain a product of 1 mmHg, a fraction at 195-196°C of 32.0 g, a yield of 92.8%, and a GC purity of 99.5%. | 92.8% |
Safety and Hazards
| Pictogram(s) |  |
| Signal | Warning |
| GHS Hazard Statements | H302 (97.62%): Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral] H332 (92.86%): Harmful if inhaled [Warning Acute toxicity, inhalation] |
| Precautionary Statement Codes | P261, P264, P270, P271, P301+P317, P304+P340, P317, P330, and P501 (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
Other Data
| Transportation | Under the room temperature and away from light |
| HS Code | |
| Storage | Under the room temperature and away from light |
| Shelf Life | 1 year |
| Market Price |
| Druglikeness | |
| Lipinski rules component | |
| Molecular Weight | 161.206 |
| logP | 0.107 |
| HBA | 3 |
| HBD | 0 |
| Matching Lipinski Rules | 4 |
| Veber rules component | |
| Polar Surface Area (PSA) | 71.37 |
| Rotatable Bond (RotB) | 5 |
| Matching Veber Rules | 2 |
| Use Pattern |
| 1,3,6-HEXANETRICARBONITRILE CAS#: 1772-25-4 is an important electrolyte additive, and the composition of the electrolyte restricts the application of positive and negative electrode materials at high voltages. Traditional organic carbonates, such as linear carbonates like DEC, DMC, EMC, and cyclic carbonates like PC, EC, tend to undergo decomposition at high voltages [2,3]. Therefore, the development of novel organic solvents with a wide electrochemical window, high lithium salt solubility, and low toxicity has become a key focus in the development of high-voltage electrolytes. Nitrile-based organic solvents typically possess a wide electrochemical window, high anodic stability, low viscosity, and high boiling points, among other excellent characteristics [4]. Additionally, the decomposition products of solvents containing nitrile groups are generally carboxylates, aldehydes, or corresponding organic amines, eliminating the generation of toxic CN- ions during usage [5-7]. Nitrile solvents demonstrate a broad electrochemical window and are considered promising new organic solvents. However, in terms of the electrochemical performance of lithium-ion batteries, nitrile solvents still face compatibility issues with the negative electrode. The formation of a mixed system with carbonate solvents or the addition of mixed salts like LiBOB can partially alleviate this issue. |
Buy Reagent | |
| No reagent supplier? | Send quick inquiry to ChemWhat |
| Want to be listed here as a reagent supplier? (Paid service) | Click here to contact ChemWhat |
Approved Manufacturers | |
| Want to be listed as an approved manufacturer (Requires approvement)? | Please download and fill out this form and send back to approved-manufacturers@chemwhat.com |
Other Suppliers | |
| Watson International Limited | Visit Watson Official Website |
Contact Us for Other Help | |
| Contact us for other information or services | Click here to contact ChemWhat |