2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine CAS#: 67881-98-5; ChemWhat Code: 956300
Identification
| Product Name | 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine |
| IUPAC Name | 2-(2-methylprop-2-enoyloxy)ethyl 2-(trimethylazaniumyl)ethyl phosphate |
| Molecular Structure | 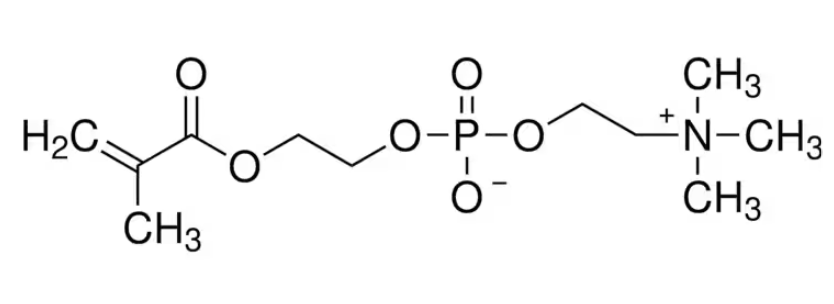 |
| CAS Registry Number | 67881-98-5 |
| EINECS Number | 207-322-2 |
| MDL Number | MFCD11112180 |
| Beilstein Registry Number | 105692 |
| Synonyms | 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholineMPC2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl 2-(trimethylammonio)ethyl phosphate |
| Molecular Formula | C11H22NO6P |
| Molecular Weight | 295.272 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C11H22NO6P/c1-10(2)11(13)16-8-9-18-19(14,15)17-7-6-12(3,4)5/h1,6-9H2,2-5H3 |
| InChI Key | ZSZRUEAFVQITHH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Canonical SMILES | C=C(C)C(=O)OCCOP(=O)([O-])OCC[N+](C)(C)C |
| Patent Information | ||
| Patent ID | Title | Publication Date |
| US2024/383865 | HIGH-ENERGY-VIOLET-ABSORBING VINYLIC MONOMERS | 2024 |
| US2017/355799 | BIOCOMPATIBLE COATINGS AND HYDROGELS FOR REDUCING FOREIGN BODY RESPONSE AND FIBROSIS | 2017 |
Physical Data
| Appearance | White to almost white Powder |
| Solubility | 83-86vol% at 20℃ and pH5.9-6.8[vol%] |
| Description (Association (MCS)) | Partner (Association (MCS)) |
| Association with compound | Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 |
Spectra
| Description (NMR Spectroscopy) | Nucleus (NMR Spectroscopy) | Solvents (NMR Spectroscopy) | Frequency (NMR Spectroscopy), MHz |
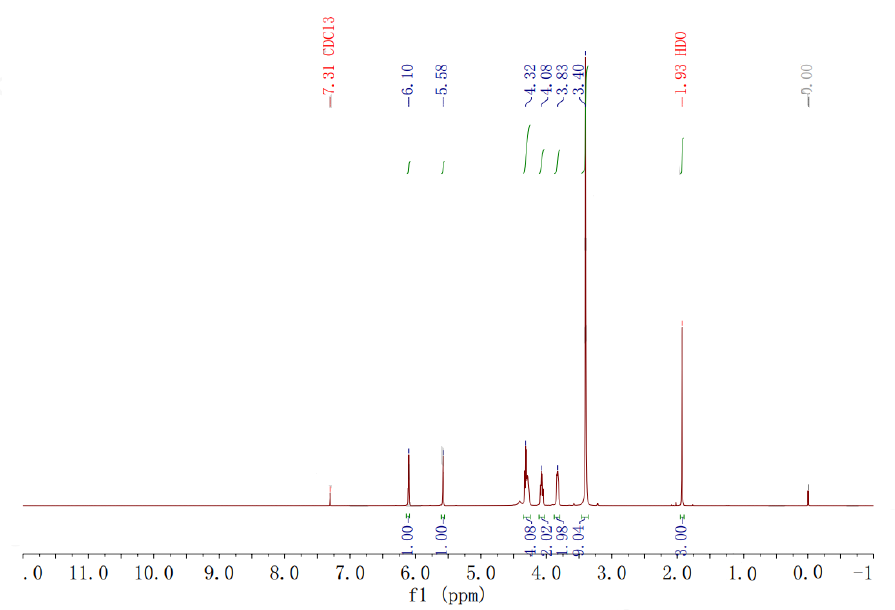
| Chemical shifts, Spectrum | 1H | water-d2 | 400 |
| Chemical shifts | 1H | chloroform-d1 | 400 |
| Description (IR Spectroscopy) | Solvent (IR Spectroscopy) | Temperature (IR Spectroscopy), °C |
| Bands, Spectrum | potassium bromide | 27 |
| Bands, Spectrum | CCl4 | 14.85 – 54.85 |
| Description (Mass Spectrometry) |
| liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LCMS), spectrum |
| Description (UV/VIS Spectroscopy) |
| Spectrum |
Route of Synthesis (ROS)
| Conditions | Yield |
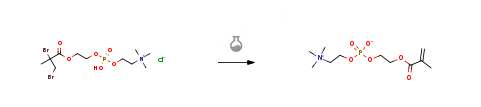
| With zinc In ethanol at 0℃; Experimental Procedure 4.2 A man-made cell membrane 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine main component synthesis method,Including the following steps: 49.2 g of bromophosphorylcholine, the white product obtained in the previous step,Dissolved in 200 ml of ethanol,The reaction was cooled to 0 ° C. Add 19 grams of zinc powder in batches,Stirring vigorously. TLC was followed until the reaction was completed.The reaction mixture was filtered, and the chloride ion was removed with the resin to remove the solvent.The residue was dissolved in dry acetonitrile and crystallized at -20 ° C.Filtration yielded the final product as a white solid,Yield 86%. | 86% |
Safety and Hazards
| Pictogram(s) |  |
| Signal | Warning |
| GHS Hazard Statements | H317 (100%): May cause an allergic skin reaction [Warning Sensitization, Skin] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. |
| Precautionary Statement Codes | P261, P272, P280, P302+P352, P321, P333+P317, P362+P364, and P501 (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
Other Data
| Transportation | NONH for all modes of transport |
| Under the room temperature and away from light | |
| HS Code | 290621 |
| Storage | Store at -20℃ for long time, Avoid hygroscopic effects. |
| Shelf Life | 2 years |
| Market Price | USD |
| Druglikeness | |
| Lipinski rules component | |
| Molecular Weight | 295.273 |
| logP | -1.043 |
| HBA | 6 |
| HBD | 0 |
| Matching Lipinski Rules | 4 |
| Veber rules component | |
| Polar Surface Area (PSA) | 94.7 |
| Rotatable Bond (RotB) | 10 |
| Matching Veber Rules | 2 |
| Use Pattern |
| MPC polymers are synthetic phospholipid polymers with zwitterionic phosphorylcholine (PC) head groups, which can form cell-membrane-like structures on various material surfaces. This special surface structure has a unique capacity to prevent nonspecific protein adsorption (NPA) and thus biofouling by the adsorption of biomolecules, cells, and other biological entities. 1.Preparation of hydrogels for use as contact lens materials and wound dressing. 2.Production of polymeric micelles and nanoparticles for drug delivery. 3.Synthesis of polymer coatings for medical devices to prevent blood clotting and bacterial adhesion. 4.Use as a monomer to prepare polymer-modified antifouling silicone hydrogel contact lenses. The addition of MPC forms a cell membrane-like structure on the contact lens and helps to prevent cell and bacterial adhesion on the surface. |
| autoimmune diseases associated with pathological inflammation |
| artificial cell membrane synthesis |
Buy Reagent | |
| No reagent supplier? | Send quick inquiry to ChemWhat |
| Want to be listed here as a reagent supplier? (Paid service) | Click here to contact ChemWhat |
Approved Manufacturers | |
| Caming Pharmaceutical Ltd | http://www.caming.com/ |
| Want to be listed as an approved manufacturer (Requires approvement)? | Please download and fill out this form and send back to approved-manufacturers@chemwhat.com |
Other Suppliers | |
| Watson International Limited | Visit Watson Official Website |
Contact Us for Other Help | |
| Contact us for other information or services | Click here to contact ChemWhat |