6-Chloronicotinic acid CAS#: 5326-23-8; ChemWhat Code: 41722
Identification
| Product Name | 6-Chloronicotinic acid |
| IUPAC Name | 6-chloropyridine-3-carboxylic acid |
| Molecular Structure | 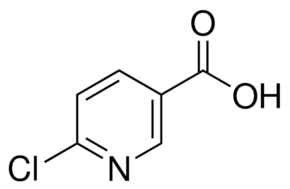 |
| CAS Registry Number | 5326-23-8 |
| EINECS Number | 226-201-5 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00006400 |
| Beilstein Registry Number | 115993 |
| Synonyms | 3-Pyridinamin;3-Pyridinamine;3-Pyridinamine;pyridin-3-amine;T6NJ CZ;3- Aminopyridine;3-Amino-pyridine;3-pyridylamine;Amino-3 pyridine;m-Aminopyridine;MS/MS-1064463;Pyridin-3-ylamine;Pyridine, 3-amino-;β-Aminopyridine 462-08-8 CAS No: 5326-23-8 CAS number: 5326-23-8 CAS#: 5326-23-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C5H6N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 94.116 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C6H4ClNO2/c7-5-2-1-4(3-8-5)6(9)10/h1-3H,(H,9,10) |
| InChI Key | UAWMVMPAYRWUFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Canonical SMILES | c1cc(ncc1C(=O)O)Cl |
| Patent Information | ||
| Patent ID | Title | Publication Date |
| EP3498694 | NEW BENZAMIDE DERIVATIVES AS PPAR-GAMMA MODULATORS | 2019 |
| WO2019/126730 | CHROMENOPYRIDINE DERIVATIVES AS PHOSPHATIDYLINOSITOL PHOSPHATE KINASE INHIBITORS | 2019 |
| US2018/230157 | PYRROLO[1,2-b]PYRIDAZINE DERIVATIVES | 2018 |
| WO2018/169373 | PYRROLOTRIAZINE DERIVATIVES AS KINASE INHIBITOR | 2018 |
| WO2018/203194 | DIAZABICYCLOOCTANE DERIVATIVES COMPRISING A QUATERNERY AMMONIUM GROUP FOR USE AS ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS | 2018 |
Physical Data
| Appearance | Light yellow flaky solid |
| Solubility | It is soluble in water as well as soluble in alcohol, benzene. |
| Flash Point | 88 ºC |
| Refractive index | 1.5560 (estimate) |
| Sensitivity | Air Sensitive & Hygroscopic |
| Melting Point, °C | Solvent (Melting Point) | Comment (Melting Point) |
| 188 | with decomposition | |
| 190 | ethanol, H2O | |
| 198 – 199 | aq. ethanol | |
| 199 | H2O |
Spectra
| Description (NMR Spectroscopy) | Nucleus (NMR Spectroscopy) | Solvents (NMR Spectroscopy) | Frequency (NMR Spectroscopy), MHz |
| Chemical shifts, Spectrum | 1H | dimethylsulfoxide-d6 | 400 |
| Chemical shifts | 13C | chloroform-d1 | |
| Chemical shifts | 1H | dimethylsulfoxide-d6 | |
| 1H | |||
| Chemical shifts | 1H | dimethylsulfoxide-d6 | 250 |
| Chemical shifts | 13C | D2O, various solvent(s) |
| Description (IR Spectroscopy) | Solvent (IR Spectroscopy) | Comment (IR Spectroscopy) |
| Bands, Spectrum | ||
| Intensity of IR bands, Bands | dimethyl sulfoxide | |
| Bands | ||
| Bands | KBr | |
| Bands | nujol | 3040 – 633 cm**(-1) |
| IR |
| Description (Mass Spectrometry) |
| spectrum |
| electrospray ionisation (ESI), spectrum |
| electrospray ionisation (ESI), time-of-flight mass spectra (TOFMS), tandem mass spectrometry, spectrum |
| electron impact (EI) |
| Description (UV/VIS Spectroscopy) | Solvent (UV/VIS Spectroscopy) | Comment (UV/VIS Spectroscopy) | Absorption Maxima (UV/VIS), nm | Ext./Abs. Coefficient, l·mol-1cm-1 |
| Spectrum | ||||
| Spectrum | aq. buffer | 224, 269 | ||
| 190, 226, 268 | ||||
| Spectrum | ethanol | 200 – 335 nm | ||
| Absorption maxima | ethanol | 251, 283.1 | 6724, 7823 | |
| UV/VIS |
| Description (NQR Spectroscopy) |
| Nuclear quadrupole resonance |
Route of Synthesis (ROS)
| Conditions | Yield |
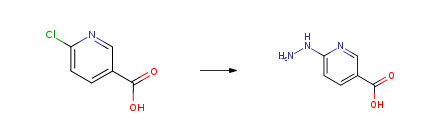
| With hydrazine hydrate at 100℃; for 4h; Inert atmosphere; Experimental Procedure 6-Chloronicotinic acid (0.30 g; 1.9 mmol) was added to a64% hydrazine monohydrate solution (2 mL, 26 mmol) andplaced at 100°C for 4h. Thereafter, the reaction mixtureturned brown and was concentrated to dryness. The residuewas dissolved in water and pH adjusted to 5.5 with concentratedHCl. A precipitate was formed, filtered and washedwith ethanol, then ether to give a yellow solid (0.346 g,96%). Mp = 292-293°C. IR (ATR, cm-1) 3210; 3058; 3039;1696; 1636; 1613; 1536-1444; 1170; 757; 736. 1H NMR(DMSO-d6) 8.63 (s, 1H); 8.07 (d, 1H, J= 9 Hz); 6.94 (d,1H, J = 9 Hz). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6) 167.2; 159.61;140.9; 119.9; 110.6. HRMS (ESI+) [M]+: 153.0531 observed,153.0538 Calcd for C6H7N3O2. | 96% |
| With hydrazine hydrate In ethanol Reflux; Experimental Procedure Example 72: 3-oxo-2,3-dihydro-[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyridine-6-carbonyl chloride; [0235] To a solution of 6-chloronicotinic acid (20 g, 127 mmol) in 200 mL of EtOH was added hydrazine hydrate (14.8 mL, 317 mmol). The mixture was refluxed overnight, then cooled to room temperature to give a solid, which was collected by filtration, washed with petroleum ether/EA (2: 1) to give 18 g of 6-hydrazinylnicotinic acid as a yellow solid (Yield: 91%). 1HNMR (DMSO, 400MHz) δ: 8.52 (s, IH), 7.88 (dd, J = 2.0 Hz, 8.8 Hz, IH), 6.63 (d, J = 8.8Hz, IH).[0236] To a suspension of 6-hydrazinylnicotinic acid (18 g, 117 mmol) in 100 mL of dry THF was added dry pyridine (23 g, 293 mmol), then the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 15 min, then bis(trichloromethyl)carbonate (80 g, 270 mmol) was added slowly. The reaction mixture was stirred overnight at room temperature, then MeOH was added and continued stirring for 15 hours to give a solid. The solid was collected by filtration and washed with petroleum ether/EA (1: 1) to give 20 g of dimethyl 3-oxo-[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3- a]pyridine-2,6(3H)-dicarboxylate. 1HNMR (CDCl3, 400MHz) δ: 3.95 (s, 3H), 4.13 (s, IH), 7.13 (dd, J = 1.6 Hz, 10 Hz, IH), 7.71 (dd, J = 1.6 Hz, 10 Hz, IH), 8.55 (t, J = 2 Hz, IH). [0237] To a solution of dimethyl 3-oxo-[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyridine-2,6(3H)-dicarboxylate (10 g, 40 mmol ) in 60 mL of THF and 10 mL of H2O was added LiOH-H2O (4.8 g, 114 mmol), and then the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 6 hours and then was concentrated in vacuo to remove THF, and then 1 mL of aq. HCl solution was added to adjust pH=2 to give a solid which was collected to give 1 Ig of compound 3-oxo-2,3-dihydro- [1 ,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid which was used without the further purification. 1HNMR (DMSO, 400MHz) δ: 7.23 (d, J = IO Hz, IH), 7.48 (dd, J = 1.6 Hz, 10Hz, IH), 8.25 (s, IH), 9.13 (s, IH), 12.89 (s, IH).[0238] To a solution of 3-oxo-2,3-dihydro-[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid (3 g, 16.8 mmol) in 60 mL of dry DCM was added oxalyl chloride (8.8 g, 74 mmol) and 1 mL ofDMF. The reaction mixture was stirred for 6 hrs at room temperature and concentrated to give[0239] 3 g of the title compound as a gray solid which was used without the further purification. | 91% |
| With hydrazine hydrate In water for 6h; Heating; | 90% |
Safety and Hazards
| Pictogram(s) |  |
| Signal | Warning |
| GHS Hazard Statements | H315 (100%): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation] H319 (100%): Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation] H335 (99.26%): May cause respiratory irritation [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure; Respiratory tract irritation] [Warning Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. |
| Precautionary Statement Codes | P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, and P501 (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
Other Data
| Transportation | NONH for all modes of transport |
| Under the room temperature and away from light | |
| HS Code | 293339 |
| Storage | Under the room temperature and away from light |
| Shelf Life | 2 years |
| Market Price |
| Druglikeness | |
| Lipinski rules component | |
| Molecular Weight | 157.556 |
| logP | 1.096 |
| HBA | 3 |
| HBD | 1 |
| Matching Lipinski Rules | 4 |
| Veber rules component | |
| Polar Surface Area (PSA) | 50.19 |
| Rotatable Bond (RotB) | 1 |
| Matching Veber Rules | 2 |
| Bioactivity |
| In vitro: Efficacy |
| Quantitative Results |
| pX | Parameter | Value (qual) | Value (quant) | Unit | Target | Effect |
| 5.2 | IC50 | 1000 | ppb | |||
| 4.04 | Ki (inhibition constant) | 91.5 | μM | Carbonic anhydrase 3:Wild | ||
| 3.52 | IC50 | = | 299 | µM | L-lactate dehydrogenase (gene ImpL3) [Plasmodium falciparum]:Wild | |
| 2.92 | inhibition rate | = | 51.1 | % | L-xylulose reductase [human]:Wild | |
| 1 | IC50(Parasite Growth) | > | 100 | µM |
| Quantitative Results | ||
| 1 of 10 | Assay Description | Solubility of compound in water was determined |
| Results | log SW not calculated | |
| Measurement | log SW | |
| 2 of 10 | Assay Description | Solubility of compound in buffer at pH 7.4 was determined |
| 3 of 10 | Assay Description | Base dissociation constant of compound was determined |
| Measurement | Base dissociation constant | |
| 4 of 10 | Assay Description | Acid dissociation constant of compound was determined |
| Measurement | Acid dissociation constant | |
| 5 of 10 | Assay Description | Effect : protein binding Target : New Zealand White rabbit polyclonal antibody Bioassay : 4-(1-<(6-chloropyridin-3-yl)-methyl>imidazolidin-2-ylidenehydrazine)-4-oxobutanoic acid-BSA conjugate used as coating antigen; percent cross-reactivity: (IC50 imidacloprid/IC50 title comp.)*100 percent in vitro; cross-reactivity to rabbit antibody evaluated using competitive inhibition ELISA; antibody raised against 4-<2(azanitromethylene)-3-<(6-chloro-(3-pyridyl)methyl>imidazolidinyl>-4-oxobutanoic acid-KLH conjugate |
| Results | cross-reactivity: <0.8 percent | |
| 6 of 10 | Biological material | mouse |
| Assay Description | Bioassay : liver microsomes | |
| 7 of 10 | Biological material | human |
| Assay Description | Bioassay : liver microsomes | |
| 8 of 10 | Assay Description | Effect : stress tolerance; effect on Target : plants comprising a transgenic gene encoding a dsRNA molecule which is capable of reducing endogenous PARG genes of Brassica sp. Bioassay : Example 2: Analysis of stress tolerance after application of neonicotinoid compounds on plants comprising a transgenic gene which increases stress tolerance. Brassica plants comprising a transgenic gene encoding a dsRNA molecule which is capable of reducing endogenous PARP genes, as described in WO |
| Results | plants treated with tested compound survive stress conditions better compared to control potential area of application: agro | |
| 9 of 10 | Assay Description | Effect : stress tolerance; effect on Target : plants comprising a transgenic gene encoding a dsRNA molecule which is capable of reducing endogenous PARG genes of rice Bioassay : Example 2: Analysis of stress tolerance after application of neonicotinoid compounds on plants comprising a transgenic gene which increases stress tolerance. Brassica plants comprising a transgenic gene encoding a dsRNA molecule which is capable of reducing endogenous PARP genes, as described in WO |
| Results | plants treated with tested compound survive stress conditions better compared to control potential area of application: agro | |
| 10 of 10 | Assay Description | Effect : stress tolerance; effect on Target : plants comprising a transgenic gene encoding a dsRNA molecule which is capable of reducing endogenous PARP genes of Brassica sp. Bioassay : Example 2: Analysis of stress tolerance after application of neonicotinoid compounds on plants comprising a transgenic gene which increases stress tolerance. Brassica plants comprising a transgenic gene encoding a dsRNA molecule which is capable of reducing endogenous PARP genes, as described in WO |
| Results | plants treated with tested compound survive stress conditions better compared to control potential area of application: agro |
| Toxicity/Safety Pharmacology |
| Quantitative Results |
| pX | Parameter | Value (qual) | Value (quant) | Unit | Effect |
| 1 | MIC | > | 128 | µg/mL | antibiotic agent |
| LD50 | = | 930 | mg/kg | ||
| LD50 | = | 560 | mg/kg | ||
| MMC4 | > | 128 | µg/mL | antibiotic agent |
| Use Pattern |
| 6-Chloronicotinic acid CAS#: 5326-23-8 Commonly used as basic raw materials. |
| 6-Chloronicotinic acid CAS#: 5326-23-8 commonly used as food additives |
| 6-Chloronicotinic acid CAS#: 5326-23-8 commonly used as feed additives |
Buy Reagent | |
| No reagent supplier? | Send quick inquiry to ChemWhat |
| Want to be listed here as a reagent supplier? (Paid service) | Click here to contact ChemWhat |
Approved Manufacturers | |
| Watsonnoke Scientific Ltd | http://www.watsonnoke.com/ |
| Want to be listed as an approved manufacturer (Requires approvement)? | Please download and fill out this form and send back to approved-manufacturers@chemwhat.com |
Other Suppliers | |
| Watson International Limited | Visit Watson Official Website |
Contact Us for Other Help | |
| Contact us for other information or services | Click here to contact ChemWhat |