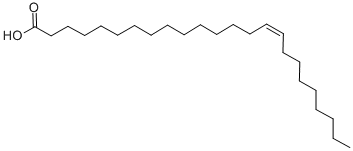
Nervonic acid CAS#: 506-37-6; ChemWhat Code: 59032
Identification
| Patent Information | ||
| Patent ID | Title | Publication Date |
| CN115417759 | Method for preparing nervonic acid from erucic acid oxidation-reduction active ester | 2022 |
| US5959131 | Nutritionally superior fat for food compositions | 1999 |
Physical Data
| Appearance | Oily or white powder |
| Melting Point, °C | Solvent (Melting Point) |
| 41.2 | |
| 40 – 41 | |
| 40.5 – 42.1 | acetone |
| 42.87 | |
| 39 | |
| 41.1 | acetone |
| 40.5 – 41 | acetone |
| Boiling Point, °C |
| 225 – 235 |
| Density, g·cm-3 |
| 0.95 |
Spectra
| Description (NMR Spectroscopy) | Nucleus (NMR Spectroscopy) | Solvents (NMR Spectroscopy) |
| Chemical shifts, Spectrum | 1H | chloroform-d1 |
| Chemical shifts, Spectrum | 13C | chloroform-d1 |
| Chemical shifts | 1H | chloroform-d1 |
| Chemical shifts | 13C | chloroform-d1 |
| Description (IR Spectroscopy) | Solvent (IR Spectroscopy) | Temperature (IR Spectroscopy), °C |
| Bands | ||
| Bands | chloroform, methanol | 25 |
Route of Synthesis (ROS)
| Conditions | Yield |
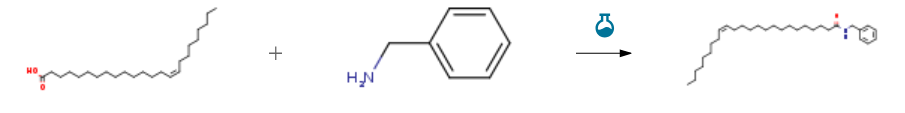
| Stage #1: Nervonic acid With 1,1′-carbonyldiimidazole In dichloromethane at 20℃; for 2h; Stage #2: benzylamine With dmap In dichloromethane at 20℃; for 18h; Experimental Procedure 4.1.1. N-benzylpalmitamide (3a) General procedure: To a solution of palmitic acid (300mg, 1.17mmol) in dichloromethane (DCM, 10mL) was added 1,1′-carbonyldiimdazole (209mg, 1.29mmol). The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 2h. The reaction mixture was slowly added to a solution of benzylamine (153μL, 1.40mmol) and 4-dimethylaminopyridine (14mg, 0.12mmol) in dichloromethane (5mL). The solution was stirred at room temperature for 18h. DCM (100mL) and saturated aqueous NaHCO3 (30mL) were added to the reaction mixture. The organic layer was separated and washed with H2O (30mL), brine (30mL), dried over anhyd sodium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure. The crude was purified by flash chromatography on silica gel eluting with hexane/EtOAc (3:1, v/v) to give the title compound as a white solid (578mg, 86%). Mp 85-87° [lit.45 mp 94.5-95°, and46 fp 95.1°]; 1H NMR (400MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.32-7.36 (m, 2H), 7.26-7.30 (m, 3H), 5.72 (br s, 1H), 4.45 (d, J=6.0Hz, 2H), 2.21 (t, J=7.2Hz, 2H), 1.61-1.67 (m, 2H), 1.25-1.34 (m, 24H), 0.88 (t, J=6.8Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 100MHz) δ 173.21, 138.66, 128.92, 128.05, 127.71, 43.80, 37.06, 32.16, 29.92, 29.89, 29.84, 29.73, 29.59, 29.56, 26.01, 22.93, 14.36; LCMS, C23H39NO, [M+H]: 346. | 94% |
| With dmap; dicyclohexyl-carbodiimide In dichloromethane at 20℃; for 1.5h; |
Safety and Hazards
| Pictogram(s) |  |
| Signal | Warning |
| GHS Hazard Statements | H315 (100%): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation] H319 (100%): Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation] H335 (100%): May cause respiratory irritation [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure; Respiratory tract irritation] |
| Precautionary Statement Codes | P261, P264, P264+P265, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P319, P321, P332+P317, P337+P317, P362+P364, P403+P233, P405, and P501 (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
Other Data
| Druglikeness | |
| Lipinski rules component | |
| Molecular Weight | 94.116 |
| logP | -0.047 |
| HBA | 2 |
| HBD | 1 |
| Matching Lipinski Rules | 4 |
| Veber rules component | |
| Polar Surface Area (PSA) | 38.91 |
| Rotatable Bond (RotB) | 0 |
| Matching Veber Rules | 2 |
| Bioactivity |
| In vitro: Efficacy |
| Quantitative Results |
| pX | Parameter | Value (qual) | Value (quant) | Unit | Target | Effect |
| 8.05 | pIC50(Virus replication) | = | 8.05 | antiviral agent | ||
| 8.05 | pIC50 | = | 8.05 | Topoisomerase dna ii 180kda (Beta) [Human immunodeficiency virus 1]:Wild | ||
| 5.65 | EC90(Amount Of P24 Protein) | > | 20 | µM | ||
| 5.48 | IC50(protease activity) | 3.3 | µM | |||
| 4.63 | IC50 | 23.45 | μg | antifungal agent | ||
| 4.59 | IC50 | 2.45 | μg/ml | antifungal agent | ||
| 4.45 | IC50 | 3.33 | μg/ml | antifungal agent | ||
| 4 | stimulation rate | Active | High voltage-activated calcium channel [rat]:Wild | |||
| 3.44 | IC50 | 34.55 | μg/ml | antifungal agent |
| Druglikeness | |
| Lipinski rules component | |
| Molecular Weight | 366.628 |
| logP | 11.606 |
| HBA | 2 |
| HBD | 1 |
| Matching Lipinski Rules | 3 |
| Veber rules component | |
| Polar Surface Area (PSA) | 37.3 |
| Rotatable Bond (RotB) | 21 |
| Matching Veber Rules | 2 |
| Use Pattern |
| Nervonic acid is an important monounsaturated fatty acid in the brain and is essential for brain health. It can help with the growth and regeneration of nerve cells, improving the function and structure of cell membranes. Although the human body can synthesize nervonic acid, the efficiency is low. Therefore, external supplementation is necessary to meet the needs of the brain and nerve development. |
Buy Reagent | |
| No reagent supplier? | Send quick inquiry to ChemWhat |
| Want to be listed here as a reagent supplier? (Paid service) | Click here to contact ChemWhat |
Approved Manufacturers | |
| Caming Pharmaceutical Limited | http://www.caming.com/ |
| Want to be listed as an approved manufacturer (Requires approvement)? | Please download and fill out this form and send back to approved-manufacturers@chemwhat.com |
Other Suppliers | |
| Watson International Limited | Visit Watson Official Website |
Contact Us for Other Help | |
| Contact us for other information or services | Click here to contact ChemWhat |