2-Furanaldehyde CAS#: 98-01-1; ChemWhat Code: 1287593
Identification
| Product Name | 2-Furanaldehyde |
| IUPAC Name | furan-2-carbaldehyde |
| Molecular Structure | 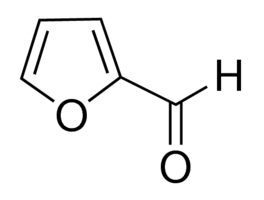 |
| CAS Registry Number | 98-01-1 |
| EINECS Number | 202-627-7 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00003229 |
| Beilstein Registry Number | 105755 |
| Synonyms | furfural, 2-furancarbaldehyde |
| Molecular Formula | C5H4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 96.084 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C5H4O2/c6-4-5-2-1-3-7-5/h1-4H |
| InChI Key | HYBBIBNJHNGZAN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Canonical SMILES | c1cc(oc1)C=O |
| Patent Information | ||
| Patent ID | Title | Publication Date |
| CN110803972 | Method for synthesizing difluoro alkyl substituted aromatic aldehyde compound under photocatalysis (by machine translation) | 2020 |
| CN111072610 | Preparation and application of substituted benzofuran 2- formyl hydrazone LSD1 inhibitor (by machine translation) | 2020 |
| CN111072594 | Preparation method 2- arylbenzothiazole compound (by machine translation) | 2020 |
| WO2020/130832 | OXIDATION OF 5-HYDROXY-2-FURANONE TO MALEATES | 2020 |
| WO2019/43414 | PROCESS | 2019 |
Physical Data
| Appearance | Colorless transparent oily liquid |
| Solubility | 95% ethanol: soluble1ML/mL, clear |
| Refractive index | n20/D 1.527 |
| Sensitivity | Air Sensitive |
| Melting Point, °C |
| -37 |
| -36.5 |
| -38.8 |
| -38.7 |
| -31 |
| 162 |
| Boiling Point, °C | Pressure (Boiling Point), Torr |
| 165 | |
| 160 | |
| 164 | |
| 68 | 12.0012 |
| 162 | |
| 161 – 162 | |
| 53 – 55 | 10 |
| Refractive Index | Temperature (Refractive Index), °C |
| 1.53133 | 9.99 |
| 1.53004 | 12.49 |
| 1.52875 | 14.99 |
| 1.52744 | 17.49 |
| 1.52617 | 19.99 |
| 1.52486 | 22.49 |
| 1.52358 | 24.99 |
| Density, g·cm-3 | Measurement Temperature, °C |
| 1.17605 | 4.99 |
| 1.17341 | 7.49 |
| 1.17075 | 9.99 |
| 1.1681 | 12.49 |
| 1.16544 | 14.99 |
| 1.16279 | 17.49 |
| 1.16013 | 19.99 |
| Description (Association (MCS)) | Solvent (Association (MCS)) | Temperature (Association (MCS)), °C |
| Adsorption | water | 22.84 |
| Adsorption | dimethyl sulfoxide | 22.84 |
| Adsorption | benzene | 22.84 |
| Adsorption | isopropyl alcohol | 20 |
| Rate of adsorption | water | 24.84 |
| Further physical properties of the adsorbed molecule | ||
| Adsorption | chloroform | 45 |
| Adsorption | H2O | 25 |
| Adsorption | aq. HCl | 25 |
Spectra
| Description (NMR Spectroscopy) | Nucleus (NMR Spectroscopy) | Solvents (NMR Spectroscopy) | Temperature (NMR Spectroscopy), °C | Frequency (NMR Spectroscopy), MHz |
| Chemical shifts | 1H | chloroform-d1 | 400 | |
| Chemical shifts | 13C | chloroform-d1 | 100 | |
| Chemical shifts, Spectrum | 1H | chloroform-d1 | 24.84 | 300 |
| Chemical shifts, Spectrum | 13C | chloroform-d1 | 125 | |
| Spectrum | 1H | benzene-d6 | 500 | |
| Spectrum | 1H | dimethylsulfoxide-d6 | 300 | |
| 2D-NMR | ||||
| Spin-spin coupling constants | CDCl3 | |||
| Spin-spin coupling constants | D2O |
| Description (IR Spectroscopy) | Solvent (IR Spectroscopy) |
| Bands | KBr |
| Spectrum | CCl4 |
| Spectrum | acetonitrile |
| Spectrum | neat liquid |
| Spectrum | CHCl3 |
| Spectrum | film |
| Spectrum | various solvent(s) |
| Bands | solid |
| Bands | neat (no solvent) |
| Bands | gas |
| Bands | CHCl3 |
| Description (UV/VIS Spectroscopy) | Solvent (UV/VIS Spectroscopy) | Comment (UV/VIS Spectroscopy) | Absorption Maxima (UV/VIS), nm | Ext./Abs. Coefficient, l·mol-1cm-1 |
| Spectrum | H2O | |||
| Spectrum | aq. H2SO4, various solvent(s) | Remark: air-saturated solution; pH 3.7, ambient temperature | ||
| aq. H2SO4, various solvent(s) | Remark: air-saturated solution; pH 3.7, ambient temperature | 276 | 16000 | |
| Absorption maxima | cyclohexane | 218, 266, 317 | 4240, 17400, 60 | |
| Absorption maxima | methanol | 218, 270, 314 | 3100, 9400, 80 | |
| Spectrum | aq. H3PO4 | 200 – 380 nm | ||
| Spectrum | ethanol | 200 – 425 nm | ||
| Spectrum | cyclohexane | 200 – 380 nm |
Route of Synthesis (ROS)
| Conditions | Yield |
| With [(pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)IrIII(4,4’-dihydroxy-2,2’-bipyridine)(H2O)]SO4; alumina; hydrogen In water at 130℃; under 22502.3 Torr; for 4h; Autoclave; Experimental Procedure 2.4. Typical experiment and product analysis 5-HMF (25.2 mg, 0.2 mmol), Cp*Ir catalyst (dissolved in H2O,5 mmol L-1, 0.04 mL, 0.1 mol%), γ-Al2O3-1 (10 mg) and H2O (3 mL)were loaded into a 10 mL stainless steel autoclave and stirred at a rateof 1000 rpm. The mixture was heated to 130 °C under 3 MPa H2 for 4 h.The liquid products were diluted with acetonitrile and analyzed by GC.Dimethyl phthalate was used as an internal standard (The typical GCcharts were showed in Supporting information Figs. S2 and S3). | 60% |
| With water; zinc at 250℃; for 2.33333h; Autoclave; | 23.1% |
| Multi-step reaction with 2 steps 1: water / 4 h / 160 °C / 750.08 Torr / Inert atmosphere; Autoclave 2: hydrogen; water / 160 °C / Autoclave | |
| Multi-step reaction with 3 steps 1: hydrogen; sodium carbonate; water / 4 h / 160 °C / 30003 Torr / pH 11 / Autoclave 2: hydrogen; water / 8 h / 160 °C / Inert atmosphere; Autoclave 3: hydrogen; water / 160 °C / Autoclave | |
| With hydrogen; copper In water at 169.84℃; under 15001.5 Torr; for 1h; Reagent/catalyst; Autoclave; chemoselective reaction; |
Safety and Hazards
| Pictogram(s) |    |
| Signal | Danger |
| GHS Hazard Statements | H301: Toxic if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral] H312: Harmful in contact with skin [Warning Acute toxicity, dermal] H315: Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation] H319: Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation] H331: Toxic if inhaled [Danger Acute toxicity, inhalation] H335: May cause respiratory irritation [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure; Respiratory tract irritation] H351: Suspected of causing cancer [Warning Carcinogenicity] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. |
| Precautionary Statement Codes | P201, P202, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P281, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P311, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P403+P233, P405, and P501 (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
Other Data
| Transportation | Class 6.1; Packaging Group: II; UN Number: 1199 |
| Under the room temperature and away from light | |
| HS Code | 293212 |
| Storage | Under the room temperature and away from light |
| Shelf Life | 1 year |
| Market Price | USD |
| Druglikeness | |
| Lipinski rules component | |
| Molecular Weight | 96.0856 |
| logP | 0.418 |
| HBA | 1 |
| HBD | 0 |
| Matching Lipinski Rules | 4 |
| Veber rules component | |
| Polar Surface Area (PSA) | 30.21 |
| Rotatable Bond (RotB) | 1 |
| Matching Veber Rules | 2 |
| Bioactivity |
| In vitro: Efficacy |
| Quantitative Results |
| pX | Parameter | Value (qual) | Value (quant) | Unit |
| 6.57 | Km (Michaelis constant)(Michaelis-menten constant) | = | 0.27 | µM |
| 5.32 | Km (Michaelis constant)(Michaelis-menten constant) | = | 4.8 | µM |
| 5.31 | Km (Michaelis constant)(Michaelis-menten constant) | = | 4.89 | µM |
| 5.14 | Km (Michaelis constant)(Michaelis-menten constant) | = | 7.2 | µM |
| 5.01 | IC50 | 9.72 | µM | |
| 4.74 | Km (Michaelis constant) | = | 18 | µM |
| 4.15 | Km (Michaelis constant) | 71.4 | µM | |
| 4.03 | IC50 | 93.1 | µM | |
| 3 | Km (Michaelis constant)(Michaelis-Menten constant towards human aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 was measured by oxidation) | = | 1000 | µM |
| 1 | IC50 | > | 100 | µM |
| 1 | LD50 | > | 100 | µg/mL |
| Quantitative Results | ||
| 1 of 10 | Effect | antimicrobial agent |
| Biological material | Bacillus subtilis | |
| Assay Description | Effect : antimicrobial Bioassay : var globi [0056] Example 2: Biocidal efficacy tests:; [0057] Tests were conducted using a South African Bureau of Standards (SABS) method (i.e. SABS1593), a Kelsey Sykes modified suspension test. The microorganism used in the test was Bacillus subtilis varglobi. The results of the tests are tabulated below:Table | |
| Results | low or no effect; synergistic effect between title compound and alcohol ethoxylate 3 surfactant; synergistic effect between title compound and alcohol ethoxylate 9 surfactant | |
| 2 of 10 | Effect | antimicrobial agent |
| Assay Description | Target : var globi of Bacillus subtilis Bioassay : [0056] Example 2: Biocidal efficacy tests:; [0057] Tests were conducted using a South African Bureau of Standards (SABS) method (i.e. SABS1593), a Kelsey Sykes modified suspension test. The microorganism used in the test was Bacillus subtilis varglobi. The results of the tests are tabulated below:Table | |
| Results | low or no effect; synergistic effect between title compound and alcohol ethoxylate 3 surfactant; synergistic effect between title compound and alcohol ethoxylate 9 surfactant | |
| 3 of 10 | Effect | radical scavenging |
| Assay Description | Inhibitory concentration of the compound against DPPH radical scavenging upon incubation for 20 mins at RT in the dark | |
| Measurement | Radical Scavenging | |
| 4 of 10 | Target | Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 [rat]:Wild |
| Biological material | rat | |
| Assay Description | Catalytic constant of compound towards rat recombinant ALDO-KETO REDUCTASE1B10 expressed in Escherichia coli to that of Michaelis-Menten constant of rat recombinant ALDO-KETO REDUCTASE1B10 expressed in Escherichia coli | |
| Results | KCAT/KM not calculated | |
| Measurement | kcat/Km | |
| 5 of 10 | Substance action on target | Inhibitor |
| Biological material | Candida albicans | |
| Assay Description | In vitro inhibitory dose against growth of Candida albicans in dextrose agar medium upon incubation for 24 h at 37 degree C by Vapor phase activity test | |
| Results | Dose not calculated | |
| Measurement | Dose | |
| 6 of 10 | Target | Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Family 1 [human]:Wild |
| Biological material | human | |
| Assay Description | Ratio of maximum velocity towards human aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 to that of Michaelis menten constant was measured by oxidation of the compound | |
| Results | Vmax/KM not calculated | |
| Measurement | Vmax/Km | |
| 7 of 10 | Target | Aldehyde dehydrogenase, mitochondrial [human]:Wild |
| Biological material | human | |
| Assay Description | Ratio of maximum velocity towards human aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 to that of Michaelis menten constant was measured by oxidation of the compound | |
| Results | Vmax/KM not calculated | |
| Measurement | Vmax/Km | |
| 8 of 10 | Target | Aldehyde dehydrogenase, mitochondrial [Saccharomyces cerevisiae]:Wild |
| Biological material | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | |
| Assay Description | Ratio of maximum velocity towards yeast aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 to that of Michaelis menten constant was measured by oxidation of the compound | |
| Results | Vmax/KM not calculated | |
| Measurement | Vmax/Km | |
| 9 of 10 | Assay Description | Bioassay : aqueous title comp. solution added to fixed bed column containing granular activated carbon at pH 7; agitated continuously for 30 h at 30 deg C; UV-spectrophotometer at 254 nm; title comp. adsorption data fitted to competitive Langmuir isotherm model |
| Results | adsorption equilibrium adsorption isotherm (qe): 0.2; maximum adsorption capacity (qm): 0.3744; adsorption equilibrium constant (b): 18.42 m3/kg; figure | |
| 10 of 10 | Assay Description | Bioassay : batch experiment; aqueous title comp. solution (0.2 kg/m3) added to fixed bed column containing granular activated carbon (3.26E-3 kg) at pH 7; agitated at 20 deg C; intraparticle diffusion coefficients of title comp. determined |
| Results | adsorption pore diffusion coefficient (Dp): 9.870E-10 m2/s; molecular diffusion coefficient (Dm): 1.04E-8 m2/s; table |
| Use Pattern |
| 2-Furanaldehyde CAS#: 98-01-1 is used asFood/food additives |
| 2-Furanaldehyde CAS#: 98-01-1 in combination with 2,4-hexadien-1-ol |
| 2-Furanaldehyde CAS#: 98-01-1 in combination with 2-methylbutanol |
| 2-Furanaldehyde CAS#: 98-01-1 in combination with 4-hexen-1-ol |
| 2-Furanaldehyde CAS#: 98-01-1 in combination with butyl acetate |
| 2-Furanaldehyde CAS#: 98-01-1 in combination with cis-4- methyl-5-butyldihydro-2(3H)-furanone |
| treating keratin fibres in combination withsugars, hydroxides and/or (hydrogen) carbonates, particular metal salts and polyphenols |
| controlling plant nematode diseases in combination with fluopyram |
| Agricultural use |
| Fumigant composition |
| production of a glycerol acetals used as solvents for polymers and resins |
| production of a glycerol acetals used as starting material for chemical synthesis where the material is reacted with materials that are capable of reacting with OH groups |
Buy Reagent | |
| No reagent supplier? | Send quick inquiry to ChemWhat |
| Want to be listed here as a reagent supplier? (Paid service) | Click here to contact ChemWhat |
Approved Manufacturers | |
| Watsonnoke Scientific Ltd | http://www.watsonnoke.com/ |
| Want to be listed as an approved manufacturer (Requires approvement)? | Please download and fill out this form and send back to approved-manufacturers@chemwhat.com |
Other Suppliers | |
| Watson International Limited | Visit Watson Official Website |
Contact Us for Other Help | |
| Contact us for other information or services | Click here to contact ChemWhat |