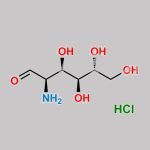
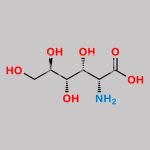
N-Acetyl Glucosamine CAS#: 7512-17-6; ChemWhat Code: 1464309
Identification
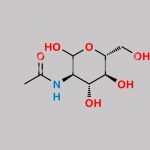
| Product Name | N-Acetyl Glucosamine |
| Molecular Structure | |
| CAS Registry Number | 7512-17-6 |
| EINECS Number | 231-368-2 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00061615 |
| Synonyms | 7512-17-6 Marine Sweet GreenNAG Bio-NAG aldehydo-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine acetyl-glucosamine N acetylglucosamine CCRIS 9357 DTXSID3045855 N-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4,5,6-tetrahydroxy-1-oxohexan-2-yl]acetamide 2-Acetamido-2-deoxyglucose EINECS 231-368-2 UNII-V956696549 NSC 400525 NSC 524344 2 Acetamido 2 Deoxyglucose N-((2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4,5,6-Tetrahydroxy-1-oxohexan-2-yl)acetamide AI3-51898 DTXCID5032369 D-Glucose, 2-(acetylamino)-2-deoxy- V956696549 NSC-400525 NSC-524344 D-Glucose, 2-acetamido-2-deoxy- N-ACETYLGLUCOSAMINE (USP-RS) N-ACETYLGLUCOSAMINE [USP-RS] MFCD00136044 NCGC00159338-02 NCGC00159338-03 N-acetylglucosamines N Acetyl D Glucosamine Glucosamine, N-acetyl- SCHEMBL19900 MLS006011606 N-ACETYL GLUCOSAMINE D- 2 Acetamido 2 Deoxy D Glucose CHEMBL4303483 N-ACETYLGLUCOSAMINE [MI] CHEBI:17411 CHEBI:59640 N-ACETYLGLUCOSAMINE [DSC] HY-A0132 Tox21_111344 BBL033994 MFCD00061615 N-ACETYLGLUCOSAMINE [WHO-DD] STK801800 AKOS005622647 DB00141 NCGC00159338-05 BP-13072 DS-18661 SMR002121580 CAS-7512-17-6 CS-0017447 S6257 A-1200 AB01325684-02 EN300-7414561 GLUCOPYRANOSE, 2-ACETAMIDO-2-DEOXY-, D- N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine-Agarose, saline suspension BRD-K80653534-001-01-7 Q32030210 1186B229-E28C-4CF9-8146-EC06A584F821 GLUCOSAMINE SULFATE POTASSIUM CHLORIDE IMPURITY A [ EP IMPURITY] 27555-50-6 |
| Molecular Formula | C8H15NO6 |
| Molecular Weight | 221.21 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C8H15NO6/c1-4(12)9-5(2-10)7(14)8(15)6(13)3-11/h2,5-8,11,13-15H,3H2,1H3,(H,9,12)/t5-,6+,7+,8+/m0/s1 |
| InChI Key | MBLBDJOUHNCFQT-LXGUWJNJSA-N |
| Isomeric SMILES | CC(=O)N[C@@H](C=O)[C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](CO)O)O)O |
Physical Data
| Appearance | White powder |
| Melting Point, °C | Solvent (Melting Point) |
| 218 | |
| 186 – 190 | ethanol, diethyl ether |
| 197 | |
| 205 – 207 | H2O |
| 205 |
| Description (Association (MCS)) | Temperature (Association (MCS)), °C | Partner (Association (MCS)) |
| Association with compound | 25 | H2O |
Spectra
| Description (NMR Spectroscopy) | Nucleus (NMR Spectroscopy) | Solvents (NMR Spectroscopy) |
| Chemical shifts | 13C | D2O |
| Spin-lattice relaxation time (T1) | ||
| Spin-spin relaxation time (T2) | ||
| NMR |
Route of Synthesis (ROS)
| Conditions | Yield |
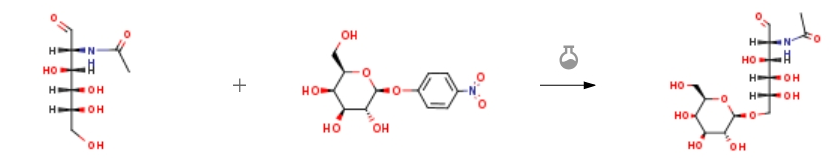
| With Biolacta N5 In N,N-dimethylhexanamide at 30℃; pH=5; aq. buffer; Enzymatic reaction; regioselective reaction; Experimental Procedure 4.5. General procedure for transglycosylation reactions using glycoconjugates General procedure: A solution of 51.2 mg (0.17 M) p-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside (donor) and 188 mg (0.85 M) of N-acetylglucosamine (acceptor) in 1 mL of green solvent (2 M)-buffer mixture was pre-equilibrated to 30 °C. Afterwards, 155 μmol/min (U) of β-galactosidase were added to the reaction mixture. Reaction was monitored by HPLC UV-vis and final products analysed by HPLC with an evaporative light scattering detector (ELSD). The reaction was stopped by heating the sample at 100 °C for 5 min.Isolation of disaccharides was done by carbon/Celite (50% m/m), chromatography, the column was eluted with milliQ water and ethanol gradient (from 5% to 15% v/v). [21] and [26] The structures of the disaccharides (Gal-β(1→4)GlcNAc and Gal-β(1→6)GlcNAc) were assigned by 1H and 13C NMR (D2O, 700 MHz), spectra were identical to previous references. [21], [26] and [27]In order to determine the effect of non-proteic substances present in Biolacta preparation in the reaction yield, transglycosylation reactions were carried out using semipurified (lyophilized) enzyme. The best performing solvents were chosen in view of the previous results, using crude extracts and setting the reactions with semipurified enzymes. The transglycosylation conditions were the same mentioned above and the reaction was monitored using HPLC-ELSD.For functionalized disaccharides the same protocol previously described was used, and different glycoconjugates as acceptors were added. A solution of 51.2 mg (0.17 M) pNP-β-Gal (donor) and the different monosaccharides functionalized 1 and 2 (0.51 M). | 86% |
| With triethyl phosphate; sodium acetate; β-galactosidase In water at 30℃; galactosylation; Enzymatic reaction; |
Safety and Hazards
| GHS Hazard Statements | Not Classified |
Source: European Chemicals Agency (ECHA)
License Note: Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: “Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/”. Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page.
License URL: https://echa.europa.eu/web/guest/legal-notice
Record Name: (1-Cyano-2-ethoxy-2-oxoethylidenaminooxy)dimethylamino-morpholino-carbenium hexafluorophosphate
URL: https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/213446
Description: The information provided here is aggregated from the “Notified classification and labelling” from ECHA’s C&L Inventory. Read more: https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database
Other Data
| Storage | Stored at room temperature for long time; Sealed and keep away from light. |
| Use Pattern |
| N-Acetylglucosamine is a versatile ingredient widely used in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, health supplements, and biomedical materials. Its primary sources include animal extraction and microbial fermentation. In the pharmaceutical field, it helps improve joint health, promotes cartilage matrix synthesis by chondrocytes, enhances cartilage repair, and alleviates joint pain. As a derivative of glucosamine, it supports skin health and tissue repair. In cosmetics, it stimulates the synthesis of hyaluronic acid (HA), enhancing skin hydration. It also repairs the skin barrier, reducing redness and sensitivity, while accelerating epidermal cell renewal and promoting wound healing. |
Related Chemicals
Buy Reagent | |
| No reagent supplier? | Send quick inquiry to ChemWhat |
| Want to be listed here as a reagent supplier? (Paid service) | Click here to contact ChemWhat |
Approved Manufacturers | |
| Want to be listed as an approved manufacturer (Requires approvement)? | Please download and fill out this form and send back to approved-manufacturers@chemwhat.com |
Other Suppliers | |
| Watson International Limited | Visit Watson Official Website |
Contact Us for Other Help | |
| Contact us for other information or services | Click here to contact ChemWhat |